Oracle Multitenant was released with Oracle 12C Release 1.
A multitenant container database, or CDB, consists of container. The root container is a collection of schemas, schema objects, and non-schema objects to which all PDBs belong.
Every CDB has one and only one root, which stores the system metadata required to manage PDBs. The root does not store user data.
A PDB is a user-created set of schemas, schema object, and related structures that appears logically to an application as separate database.
The multi-tenant architecture provide the capability to manage many database as one. Many are the benefits for DBAs from easier resource management, backups, patching and configuration for high availability and…
The non-CDB architecture is deprecated in Oracle Database 12c, and may be desupported and unavailable in a release after Oracle Database 12c Release 2. Oracle recommends use of the CDB architecture.
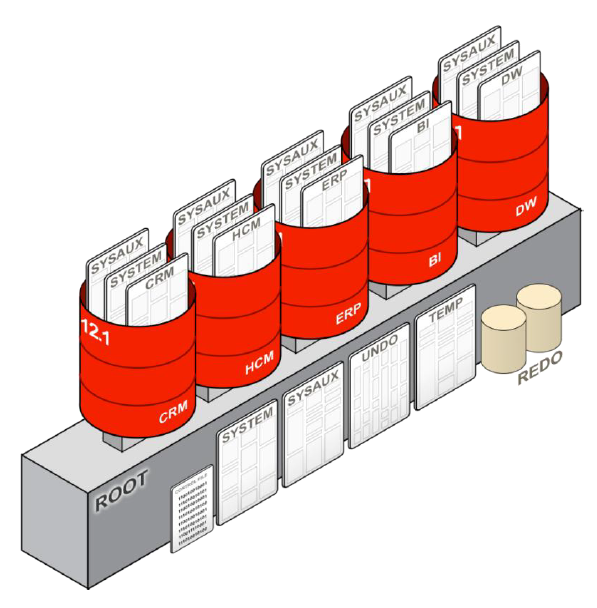
In this architecture each PDB has its own set of tablespaces including SYSTEM and SYSAUX, PDBs share UNDO, REDO and control files, (s)pfile and by default the CDB has single TEMP tablespace but PDBs may create their own.
A container is either a PDB or the root.
SQL> select name,cdb con_id from v$database;
NAME CDB CON_ID
——— — ———-
CDC YES 0
Every CDB has exactly one root…
SQL> show con_name
CON_NAME
——————————
CDB$ROOT
… and exactly one seed PDB
SQL> select pdb_name from dba_pdbs;
PDB_NAME
——————————————————————————–
PDB$SEED <—-
| Master Note for the Oracle Multitenant Option (Doc ID 1519699.1)
Oracle 12c Multitenant: Frequently Asked Questions (Doc ID 1511619.1) |